“The world would be a nicer place if everyone had the ability to love as unconditionally as dogs” – M K Clinton
Most Common Bacterial Infections in Dogs
Dogs have been known for centuries for their innumerable abilities and contributions. Studies have shown that bringing home a dog can change one’s life for the better. There is no better natural antidepressant remedy than a dog.
It is not simply possible to feed them anything we eat or treat them as we treat ourselves. For eg. dogs cannot eat cakes and chocolates nor can regular bath soap and shampoo we use can be used on them. There are many types of dog health issues. One of the most important health concerns many pet owners face is Skin infection in dogs. Sadly enough in many cases, owners only detect the issue when the situation is in a much worse condition than one would have anticipated.
What can cause skin infection in dogs?

Like humans dogs also suffer from numerous kinds of dermatological issues that are caused due to multiple reasons. The most common etiological factors that can cause skin infection in dogs include-
- Allergic reaction to pollens and environmental allergens
- Certain types of food
- Changes in the weather conditions
- Humidity
- Microbial Infection caused by viruses, bacteria, and fungus
- Ticks, mites, and fleas
- Hormonal conditions
- Underlying systemic conditions like renal and hepatic disorders
- Nutritional deficiency
- Autoimmune condition
What are the various kinds of skin infections that can occur in dogs?
Some of the most common skin conditions that are often left unseen or are neglected as simple skin itching includes
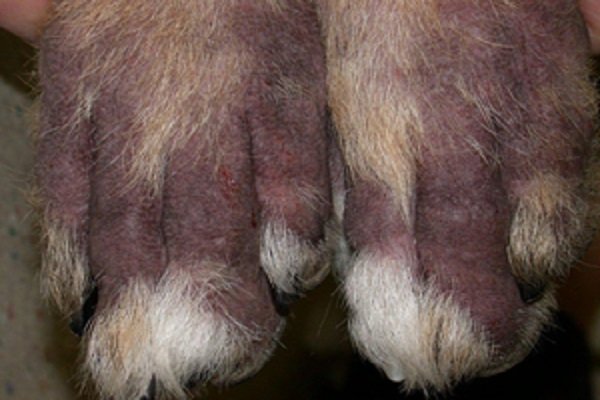
a. Atopic or Allergic Dermatitis – This is one of the most common allergic reactions seen in a dog. Caused due to allergic reaction to pollens, dust, and mites, the signs and symptoms include severe reddish patches caused by constant scratching around the eyes, muzzles, ears, and feet.

b. Alabama Rot or CRGV – This is one of the most fatal conditions with a morbidity rate of over 25% due to renal failure. Caused due to E. Coli Bacteria, the initial symptoms include red color lesions and patches all over the limbs, chest, and abdomen area.

c. Folliculitis –
A very common yet hidden skin, Folliculitis presents itself in the form of scabs and sores on the skin. Folliculitis is often seen with Mange, Allergic reactions, and injuries. Though easy to detect in short hair breeds, it often goes unseen in long or double-coat breeds. They are painful and repeat scratching on the scabs can result in microbial infections.
Download Monkoodog PetCare App
d. Lick granuloma or Acral granuloma – is caused due to constant licking of a specific area. A psychological issue caused due to certain underlying causes, Lick granuloma presents itself as fiery red ulcerated patches around the limbs.
e. Dry skin and hypopigmentation – Generally caused due to deficiency of vitamins and minerals, this condition presents itself as flaky and cracked skin. Reduced skin keratinization causes these cracks and skin shedding. If left untreated these areas become the primary area for microbial breeding.

f. Seborrhea – A common condition caused due to hormonal changes or any other underlying situation, it presents itself as dandruff and greasy skin condition. If left untreated it can cause a multitude of other issues.
g. Ringworm –
Contrary to its name, the disease is not caused due to any worm. Highly contagious in nature this fungal infection presents itself as small patches of alopecia or hair loss with inflammation or scabs and rash-like conditions. It is commonly seen in and around the paws, ears, muzzle, abdomen, and back.

h. Sarcoptic Mange – Also known as canine scabies, it is caused due to parasitic mites. Severe itching, red sores, scabs, and severe hair loss are some of the main signs of this skin condition.
i. Fleas and Ticks related skin conditions – These are external parasitic insects that live on the surface of the host to suck the blood for nutrition. Severe itching, scabs wounds, lesions, and anemia are the initial symptoms of the disease. Intense licking and weight loss are the predominant signs of Flea and tick infection.
j. Dermal Changes – Change in the skin texture to rough and dry flaky condition or color changes around the limbic joint area can be caused due to metabolic discrepancy. There are many dangerous foods for dogs that can cause severe hormonal imbalance and metabolic disorders a dog which leads to dermal changes.
How should skin infections in dogs be treated?
Some of the most common treatment methods used for treatment include
- Antibacterial treatment – systemic and topical
- Antifungal treatment- systemic and topical
- Hormonal therapy
- Nutritional Supplementation
- Anthelmintic treatment
- Topical application of medicinal oils, ointments, and gels
- Chlorhexidine bath
- Dietary modification
Preventive measures to keep Canine skin infections at bay

Skin infection in dogs can be prevented. Simple rules, when implemented strictly, can prevent the rise of this kind of issue in dogs.
Along with maintaining a very hygienic and clean environment, dogs should be fed a well-balanced diet. Make sure their diet doesn’t contain any allergic food ingredients to them. This improves its internal immunity to a great deal and promotes a better overall systemic development.
- Optimal humidity prevents drying of skin while a well-ventilated living space prevents the proliferation and growth of unwanted microbial elements.
- Regular bath and cleaning of the limbs with antibacterial dog products keep fleas and mites at bay.
- Supplementing their regular diet with additional vitamins and mineral capsules helps in boosting their immunity further.
It is important to know that these voiceless innocent beings cannot tell us their problems or issues when we do feed or do something wrong. That’s why it is important to always be very attentive to even the smallest change in their mannerism and habits to know if anything is troubling them.
Remember that a happy and healthy dog will always be active and boisterous while a sick one will prefer whining, sleeping, or just being distant.

